Pavilion Georgetown KY: Your Fun & Fitness Hub
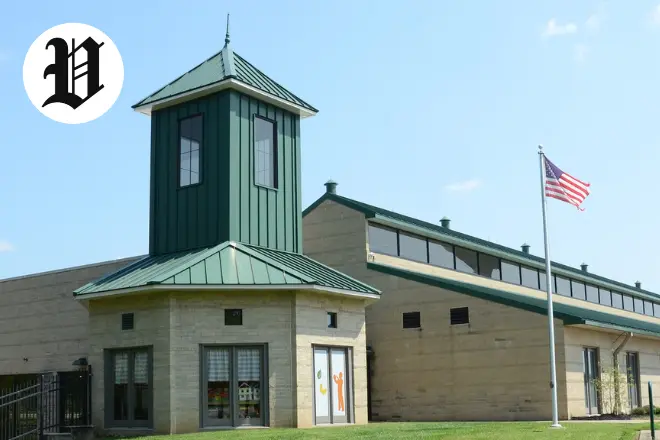

Ever feel like you need one perfect spot to swim, work out, and hang out with the community? That’s exactly what the Pavilion Georgetown, KY brings to the table. It’s become the go-to place for locals who want fitness and fun without the hassle.
You’ll spot the Pavilion Georgetown at 140 Pavilion Drive, smack in the center of Scott County. It ties right into the Georgetown-Scott County Parks and Recreation vibe. Folks keep searching for the Pavilion Georgetown Kentucky because it truly has a bit of everything for kids, adults, and everyone in between.
What Makes the Pavilion Georgetown Stand Out?
Think of the Pavilion as your all-in-one spot for staying active and connected. You’ve got these fantastic indoor areas built for health and good times. It’s set up to welcome people of all ages and fitness levels, helping you build habits that stick.People rave about how spotless it is and how welcoming the team feels. Step inside, and you instantly get that sense of belonging. The whole layout just invites you to jump in, whether you’re trying something new or sticking to what you love.
Dive into the Pavilion Aquatic Center
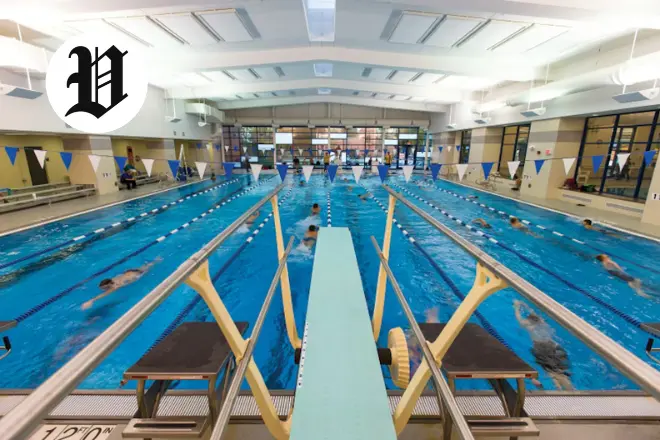

If swimming’s your thing, you’ll love what the Pavilion Aquatics Center offers. Jump into the eight-lane competition lap pool for those focused swims or easygoing laps. The water’s always just right, so you can keep at it no matter the season.
Right beside it, the leisure pool comes with a whirlpool to unwind in. Slide down the 108-foot thrill ride, which kids and families can’t get enough of. The Pavilion pool creates this welcoming environment where safety and enjoyment go hand in hand.
Those hunting for a Pavilion Georgetown KY indoor pool often land here. Being indoors means you swim anytime, rain or shine. Forget about waiting for summer; focus on your routine instead.
Fitness and Gym Facilities at the Pavilion Center
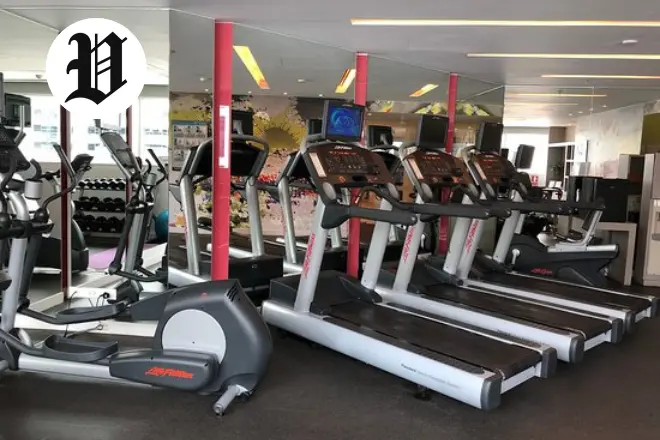

On the hunt for gyms in Pavilion Georgetown KY? The Pavilion gym steps up with its solid fitness center. You’ve got free weights, machines for resistance, and all the cardio gear like treadmills and bikes.
Up above, an indoor walking track lets you stroll or power walk with a view of the action below. It keeps things interesting as you move. This variety helps you switch up your workouts and stay motivated.
At the Pavilion recreation center, group classes happen in dedicated spaces. You can hop into yoga or aerobics to boost your strength and bendiness. Participants in Silver Sneakers Georgetown KY love the programs designed just for them.
People also see: Top Tourist Places in Las Vegas to Explore
Sports Courts and More at the Pavilion Georgetown
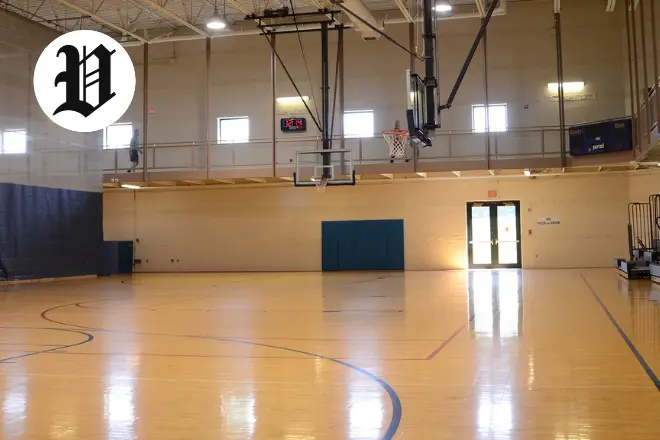

For basketball fans, the two regulation courts are a dream. Pick up a game or dive into a league in this big gym. It buzzes with tournaments and team practices, full of that competitive spirit.
You can switch to volleyball or other sports in the same area too. The Pavilion basketball court pulls in school teams from around. It’s where young athletes and groups come together for the love of the game.
Outside, Pavilion Park adds that fresh-air touch with its playground and open areas. Mixing indoor and outdoor like this makes the Pavilion Georgetown community center so flexible for whatever you’re in the mood for.
Pavilion Hours: When to Plan Your Visit
Knowing Pavilion hours helps you make the most of your day. It kicks off early for those dawn workouts and runs late enough for evening visits. Keep an eye out for any tweaks due to special events.Here’s how the typical schedule breaks down:
| Day | General Hours | Pool Hours (School Session) |
|---|---|---|
| Monday-Friday | 5:30 AM – 9:30 PM | 5:30 AM – 1:00 PM / 4:00 PM – 8:30 PM |
| Saturday | Varies by season | Check website for details |
| Sunday | 12:00 PM – 6:00 PM | 12:00 PM – 6:00 PM |
Pavilion pool hours open up more during school breaks for all-day fun. Double-check the latest to fit it into your plans, especially if you’re heading to the Pavilion Georgetown KY pool.
How to Become a Pavilion Member
Getting a Pavilion membership means easy access whenever you want, plus some extra bonuses. Pick the plan that fits you best, like individual, family, or senior options. If you’re just testing the waters, grab a daily pass.
Even companies get in on it with group memberships to boost team health. Signing up’s straightforward at the desk. No big commitments upfront.
Once you’re a Pavilion member, classes and events become yours first. It really amps up your time at the Pavilion Georgetown aquatic center and all around the facility.
Programs and Events at the Pavilion Indoor Facility
The calendar at this place is always buzzing with stuff to do. Take swimming lessons at the Pavilion Georgetown swimming pool to sharpen your skills, no matter your level. The teachers emphasize staying safe while getting better.
Fitness options go from intense sessions to calmer ones. Give Zumba a shot or build muscle with weights. Over at the Pavilion swim center, aqua classes in the water are gentle on your body.
Events pull the community closer. Show up for holidays, clinics, or wellness days. It’s all about building those local bonds in Pavilion Georgetown KY.
Kids thrive with the youth setups. Sign them up for camps or sports at the Pavilion center pool and courts. Perfect for keeping them busy after school.Seniors find programs that keep them going strong. Join fitness tailored for you or just chat with others. The indoor pool Pavilion Georgetown KY is great for soothing water sessions.
Why You Should Visit the Pavilion Georgetown
What I love about the Pavilion is how it simplifies life. Handle your workout, playtime, and family outings without running around town. Everything’s right there.
It’s easy on the wallet too. Fees stay fair for what you get. Way better bang for your buck than fancy private spots.
Your health gets a real lift from regular stops. Mixing activities keeps it fresh, helping you commit long-term.
It strengthens the whole area too. By showing up, you back local fun and fitness. Scott County feels more connected because of it.
Families call it a winner. Kids play while you sneak in exercise. Flip through Pavilion Georgetown photos, and you’ll see all the happy faces.
If you’re into sports, the setups are pro-level. Train in the lap pool or shoot hoops. It’s your starting point for hitting personal bests.
Even if you’re just chilling, it’s relaxing. Soak in the whirlpool after a long day. The atmosphere makes every visit feel good.
Everyone can get around easily here. Features make it open to all. That’s the thoughtful design at work.
Come winter, it’s a lifesaver. Beat the chill at the indoor pool in Georgetown KY. Summers tie in the park for even more options.
They keep improving based on what you say. Staff pays attention and makes changes. It stays relevant that way.
FAQ
What facilities does the Pavilion in Georgetown KY offer?
You access indoor pools, a gym, basketball courts, a walking track, and meeting rooms. The Pavilion aquatic center includes a lap pool and leisure area with a slide.
How do I find Pavilion hours?
You check the general schedule: Monday through Friday from 5:30 AM to 9:30 PM, with adjusted pool times. Pavilion pool hours extend when schools are out.
What are the options for Pavilion membership?
You select from individual, family, senior, or corporate plans. Pavilion members enjoy unlimited access and class priorities.
Is there a Georgetown KY swimming pool at the Pavilion?
Yes, the indoor Georgetown swimming pool features an eight-lane lap area and a leisure section. It’s perfect for year-round use.
Can I use the Pavilion gym?
You work out in the fitness center with weights, machines, and cardio gear. It’s one of the top gyms in Georgetown KY.
What activities happen at the Pavilion center?
You join swimming lessons, fitness classes, sports leagues, and community events. The Pavilion recreation center hosts diverse programs.
How much does it cost to visit the Pavilion Georgetown Kentucky?
You pay for daily passes or opt for affordable memberships. Rates vary by type, supporting accessible recreation.
Are there indoor pools in Georgetown KY?
The Pavilion provides a key indoor pool Georgetown KY option. You swim in controlled conditions anytime.
What makes the Pavilion pool special?
You enjoy the whirlpool, slide, and competition lanes. The Pavilion swimming pool caters to fun and fitness.
Can seniors join programs at the Pavilion?
You participate in Silver Sneakers Georgetown KY sessions and other tailored activities. The facility welcomes all ages.




One Comment